About Vitamins
What They Are Vitamins: Vitamins are organic compounds your body needs in small amounts to function properly. Most vitamins cannot be made by the body in sufficient quantities, so they must come from food or supplements.
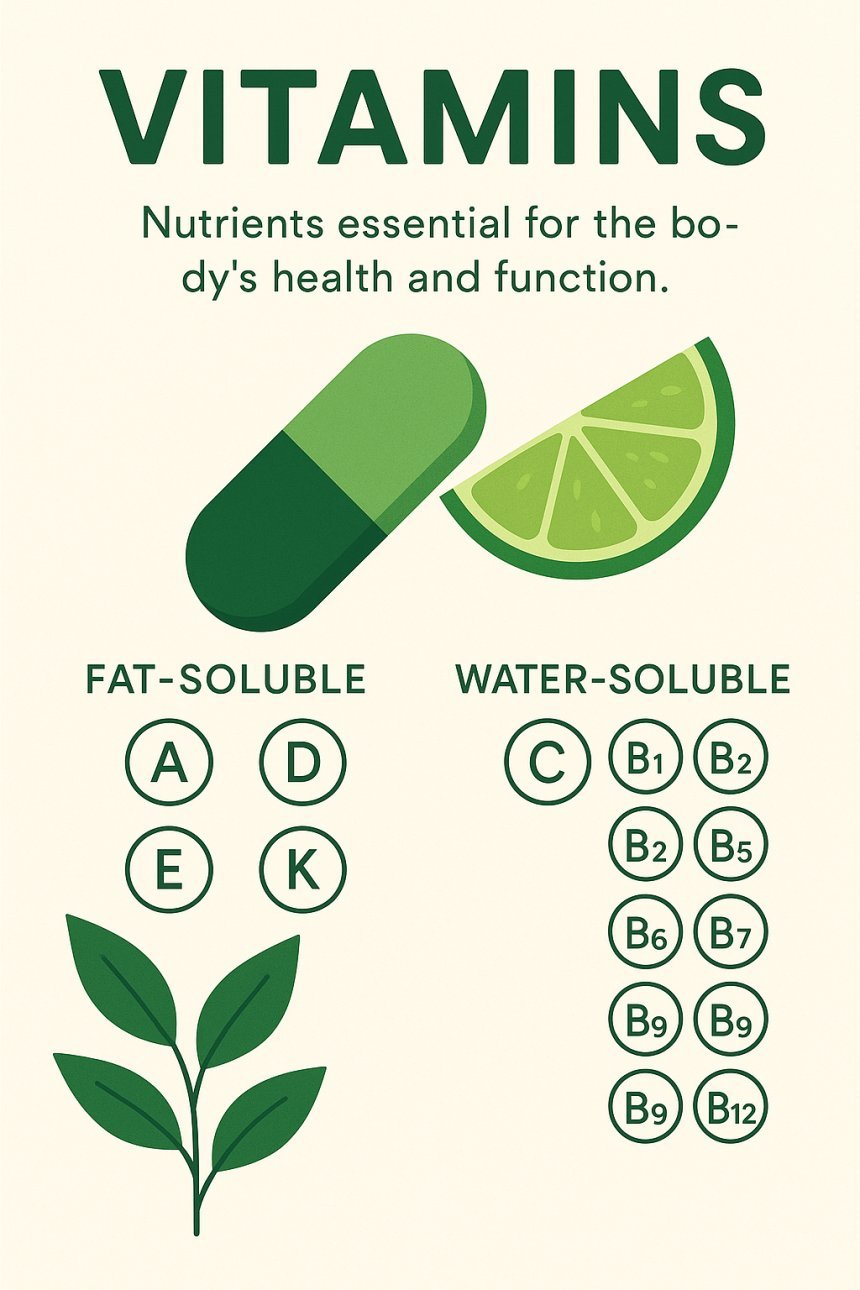
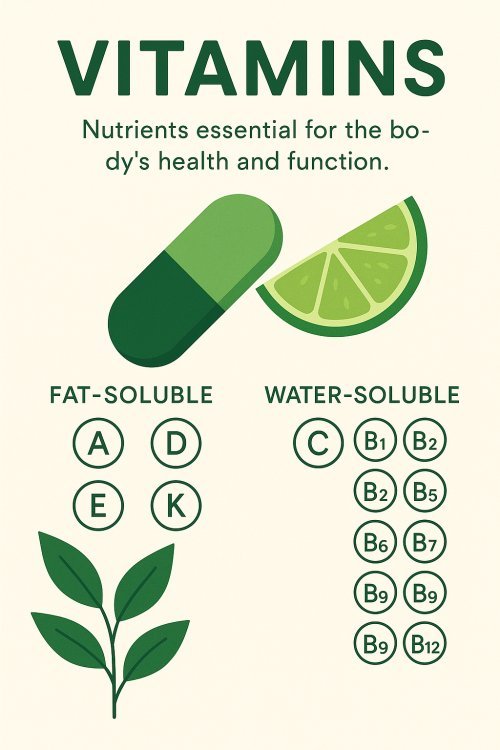
Types of Vitamins:
Vitamins are divided into two main categories:
1. Fat-Soluble Vitamins (stored in the body's fat)
-
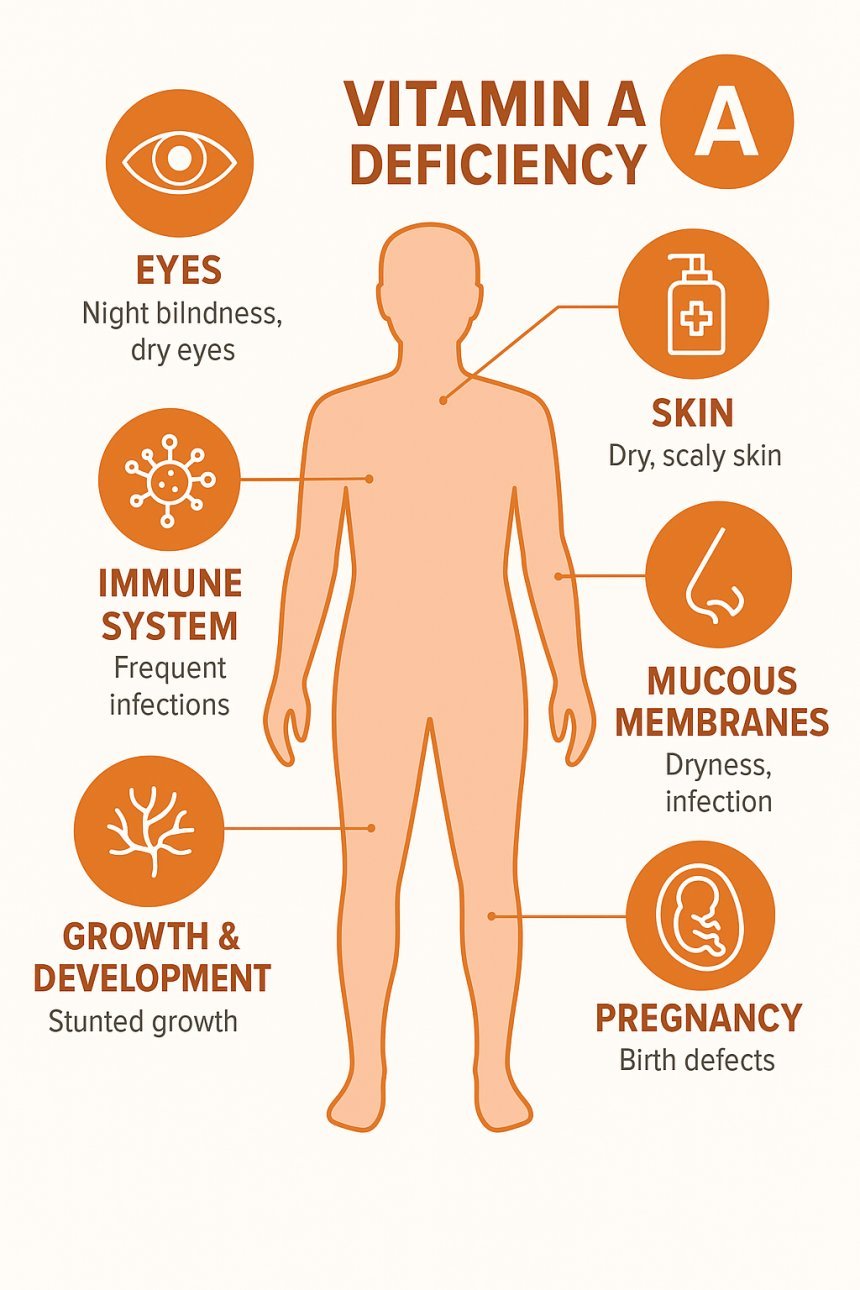
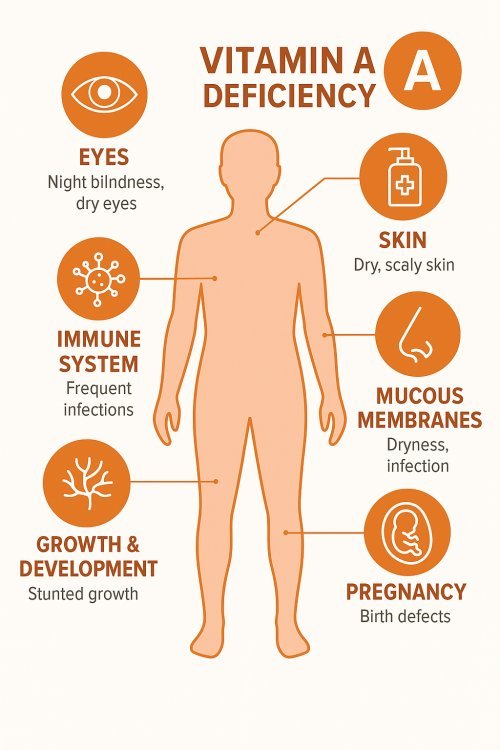
Vitamin A – Vision, immunity, skin health
-
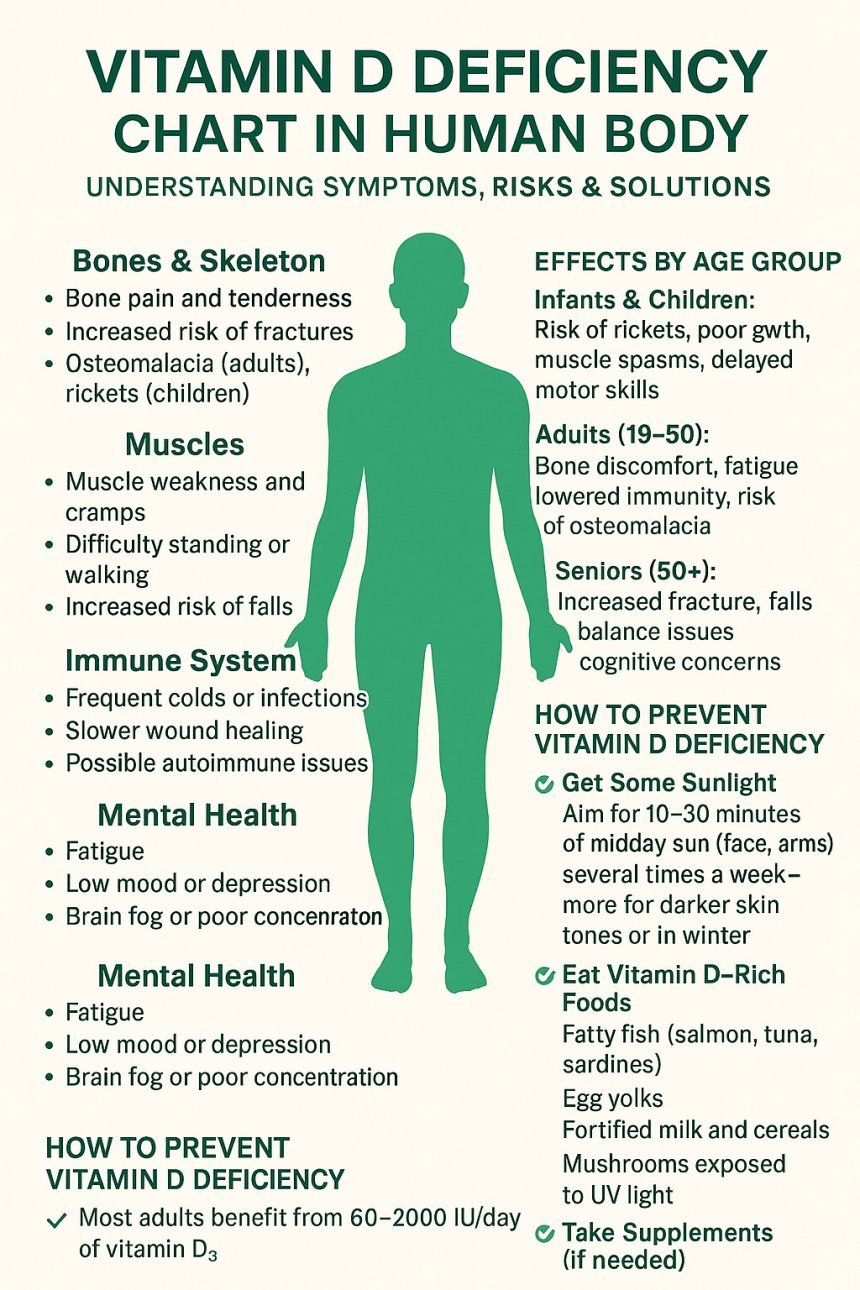
Vitamin D – Bone health, immune function
-
Vitamin E – Antioxidant, skin repair
-
Vitamin K – Blood clotting, bone health
2. Water-Soluble Vitamins (not stored, need regular intake)
-
Vitamin C – Immunity, antioxidant, skin repair
-
B Vitamins Group:
-
B1 (Thiamine) – Energy metabolism
-
B2 (Riboflavin) – Cellular function
-
B3 (Niacin) – Cholesterol, skin, nerves
-
B5 (Pantothenic Acid) – Hormone synthesis
-
B6 (Pyridoxine) – Brain development, metabolism
-
B7 (Biotin) – Hair, skin, nails
-
B9 (Folate/Folic Acid) – DNA synthesis, pregnancy health
-
B12 (Cobalamin) – Nerve function, red blood cells
-
Why Vitamins Matter:
-
Support immune function
-
Promote energy production
-
Aid in healing, repair, and growth
-
Prevent deficiencies that can lead to diseases like scurvy (Vitamin C) or rickets (Vitamin D)
Sources of Vitamins:
-
Fruits & Vegetables – C, A, K, folate
-
Whole Grains – B vitamins
-
Dairy & Eggs – D, B12, A
-
Nuts & Seeds – E, B7
-
Sunlight – Vitamin D synthesis
-
Supplements – When diet alone is insufficient
Caution:
-
More isn’t always better. Excess fat-soluble vitamins can build up and cause toxicity (e.g., too much Vitamin A or D).
-
Always consider bioavailability, interactions with medications, and whether supplements are needed.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0